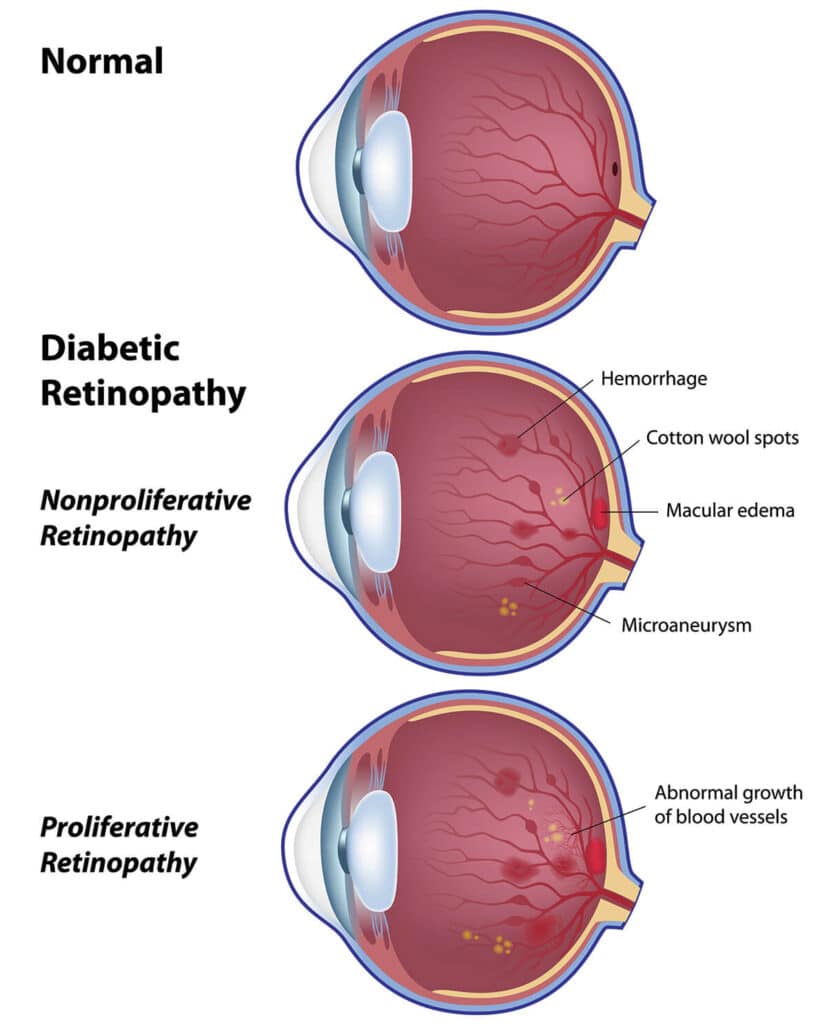
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetes mellitus is the most common cause of blindness in people younger than 65 years of age and one of the leading causes of permanent decreased vision. An estimated 41 million people in the United States alone, 40% of which are adults ranging in age of 40 – 74 years, have “pre-diabetes,” a condition that significantly increases their risk of developing diabetes.
High blood sugars and abnormalities in metabolism in diabetes mellitus may damage the blood vessels in the retina. Some of the most sensitive tissues to decreased blood flow and oxygen delivery include the brain, the heart, the kidneys and the eyes.
Treatment
Surgical treatment of a diabetic eye disease most commonly involves treatment of the retina with an argon laser.
- For Background Diabetic Retinopathy, Focal / Macular photocoagulation or grid macular photocoagulation is performed.
- During treatment for Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy, the entire retina except for the center, is treated with a laser to decrease the leaking of blood vessels and growth of unwanted new blood vessels.
- If extensive growth of new blood vessels, extensive scar tissue formation, tractional retinal detachment, or severe bleeding inside the eye has occurred, a vitrectomy is performed. In some instances, a vitrectomy combined with laser treatment and/or retinal detachment surgery is required.